A logistics facility in Ohio spent $8,000 every year regrading and replenishing their traditional gravel parking lot. Ruts formed monthly. Gravel migrated into landscaping. Puddles appeared after every rain. After installing a BaseCore HD geocell system, they haven’t touched the surface in five years—and the HDPE material is engineered to provide 75+ years of ground stabilization.
If you’ve been searching for solutions to gravel that won’t stay put, erosion that keeps returning, or parking areas that turn into muddy disasters, you’ve likely encountered the term “geocells.” But what exactly are they? How do they work? And are they the right solution for your specific challenge?
This guide answers every question first-time researchers ask about geocell technology. You’ll understand the engineering principles, discover real-world applications, learn the technical specifications that matter, and understand how to evaluate whether geocells make sense for your project.
What Geocells Actually Are: Understanding the Technology

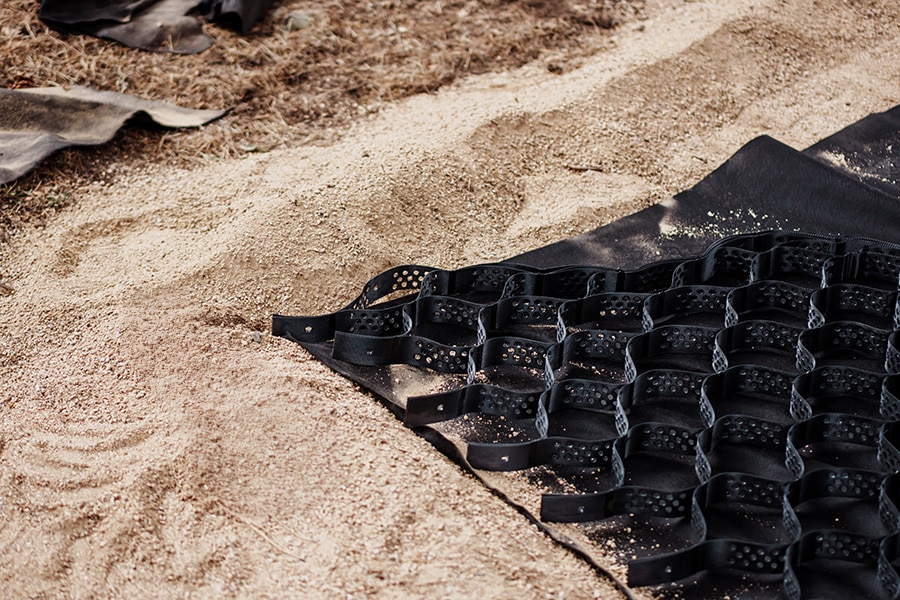
Geocells are three-dimensional honeycomb structures made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that create individual containment cells for infill materials like gravel, soil, or aggregate. Think of them as a permanent framework that transforms loose material—which naturally shifts, migrates, and fails under load—into a stable, load-bearing surface engineered to last 75+ years.
The concept originated from military engineering needs. In the 1970s, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers developed early cellular confinement systems to solve a persistent problem: building roads and helicopter landing pads quickly on soft sand in beach landing operations. Traditional methods required hauling in massive quantities of material or accepting surfaces that deteriorated rapidly under heavy military vehicles.
The engineering insight was elegant. Instead of fighting the tendency of loose materials to spread under load, why not physically contain them? By confining sand or gravel within individual cells, the material couldn’t migrate laterally. Load from vehicles distributed across multiple cells rather than concentrating at tire contact points. The contained material acted as a unified structural system rather than individual particles.
Modern geocells evolved from those military origins into sophisticated ground stabilization systems used across commercial, industrial, residential, and military applications worldwide. The fundamental principle remains unchanged: cellular confinement transforms loose materials into stable surfaces.
How the Honeycomb Structure Creates Stability
Understanding why geocells work requires understanding why loose gravel fails. When a vehicle drives over unconsolidated gravel, each tire concentrates thousands of pounds of force onto a small contact area. The gravel particles beneath the tire push downward and outward, displacing adjacent particles. Over time, this creates ruts where tires repeatedly travel and berms where displaced material accumulates.
Water compounds the problem. It infiltrates through the disturbed surface, softens the subgrade beneath, and accelerates the rutting cycle. What started as a minor depression becomes a pothole. The pothole collects more water. The cycle accelerates.
Geocells interrupt this failure pattern through three engineering mechanisms that work simultaneously.
The first mechanism is lateral confinement. Each cell wall physically prevents gravel from moving sideways. The particles that started in a particular cell stay in that cell, regardless of the load applied above. Gravel can compress vertically within the cell, but it cannot migrate laterally to create ruts or bare spots.
The second mechanism is load distribution. The interconnected cellular structure spreads each tire’s weight across multiple cells rather than concentrating it at the contact point. Engineers describe this as the “snowshoe effect”—the same weight distributed across a broader area creates less pressure per square inch on the subgrade below. This prevents the point-loading that pushes material into soft subgrade and initiates rutting.
The third mechanism is vertical stiffening. The cell walls themselves provide structural resistance. Under load, the walls experience tension forces that resist deformation. The confined aggregate and the HDPE walls work together as a composite system stronger than either material alone.
Why Material Quality Determines Long-Term Performance
Not all geocells deliver equal performance. The difference between a system that provides 75+ years of ground stabilization and one that fails prematurely comes down to material quality and manufacturing standards.
BaseCore geocells are manufactured from 100% virgin HDPE—not recycled materials that introduce inconsistencies and weaknesses into the polymer structure. Virgin HDPE delivers predictable, consistent performance characteristics that engineers can rely on for decades of service.
Material thickness directly affects load capacity and durability. Thicker cell walls resist the lateral forces from confined aggregate under heavy loads without deforming or failing. BaseCore HD, the commercial and military grade product, uses 2.4mm thick material—significantly thicker than many alternatives in the market that use thinner materials to reduce costs at the expense of performance.
The cell-to-cell connections represent critical stress points in any geocell system. When adjacent cells experience different loads—such as when a tire straddles the boundary between cells—the welds must withstand significant tension forces. Weak welds create failure points that propagate into larger system failures.
BaseCore HD features double-welded seams that deliver superior seam peel strength of 88 lbf/in minimum, with long-term seam strength rated at 190 lbs. This double-weld construction provides redundancy and strength that single-weld alternatives cannot match.
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) measures how well the HDPE resists cracking under sustained stress over time. BaseCore HD achieves 7,000 hours of ESCR per ASTM D-1693 testing—exceeding the 5,000 to 6,000 hour ratings typical of other products. This superior crack resistance translates directly to longer service life in demanding applications.
Understanding BaseCore and BaseCore HD: Two Product Lines for Different Applications
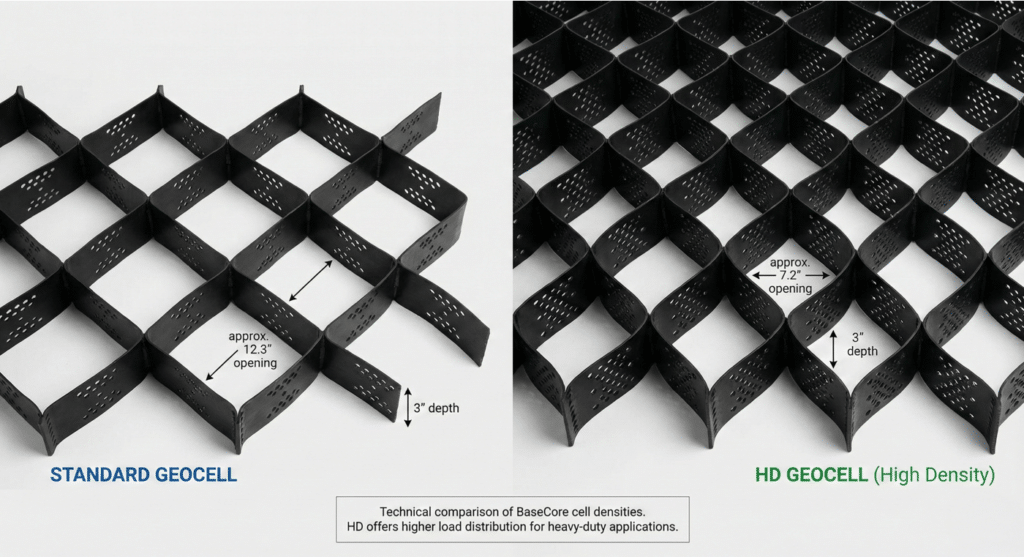
BaseCore manufactures two distinct geocell product lines engineered for different application requirements. Understanding the differences helps you select the right system for your specific needs.
BaseCore: The Standard Residential Grade
Standard BaseCore geocells are designed for residential and light-duty applications where extreme load capacity isn’t required. The specifications include 1.7mm reinforced material thickness with 445mm weld spacing and an expanded cell size of approximately 12.3 by 10.3 inches.
This configuration works well for residential driveways with passenger cars, walkways and pedestrian areas, light landscaping applications, and moderate slope erosion control. The larger cell size covers area efficiently and keeps material costs reasonable for applications that don’t demand maximum strength.
BaseCore HD: Commercial and Military Grade
BaseCore HD represents the heavy-duty product line engineered for commercial, industrial, and military applications. The specifications reflect this demanding use case: 2.4mm heavy-duty material thickness with 260mm weld spacing and an expanded cell size of approximately 7.2 by 6.0 inches.
The HD designation indicates several critical upgrades. The cell density is 35% higher than standard BaseCore, meaning more cell walls per square foot providing greater confinement and load distribution. The double-welded seams deliver tensile strength exceeding 2,000 pounds per square foot. The thicker material and tighter weld spacing create a system capable of supporting the heaviest commercial and military vehicles.
BaseCore HD suits commercial parking lots, industrial yards with semi-truck traffic, military installations, oil and gas operations, mining applications, fire lanes and emergency access, and any application where failure isn’t acceptable.
Selecting the Right Product Line
The selection between BaseCore and BaseCore HD comes down to your load requirements and risk tolerance. For residential applications with passenger vehicles only, standard BaseCore provides excellent performance at lower cost. For any commercial or industrial application—or residential applications where occasional heavy vehicles like delivery trucks or moving vans will access the surface—BaseCore HD delivers the strength and durability to handle demanding loads over decades of service.
When in doubt, specify BaseCore HD. The incremental cost is modest compared to the cost of premature failure or the need to restrict vehicle access to protect an underspecified system.
Cell Depth Specifications and Load Capacity
Cell depth—the height of the geocell walls—is the primary specification affecting load capacity. BaseCore manufactures geocells in depths of 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 inches, with the ability to customize other sizes for specific project requirements.
Load Capacity by Depth
The relationship between cell depth and load capacity follows engineering principles: deeper cells provide more lateral confinement and better load distribution, enabling support for heavier vehicles.
At 75mm (3 inches), geocells support gross vehicle weights under 1,000 kg, suitable for pedestrian paths, bicycle lanes, and light recreational use.
At 100mm (4 inches), capacity increases to under 3,000 kg gross vehicle weight, appropriate for domestic traffic with passenger cars only.
At 100-150mm (4-6 inches), the system handles under 6,000 kg for car parks with cars and light vans, or under 9,000 kg for delivery van traffic.
At 150mm (6 inches), capacity reaches under 16,000 kg, supporting emergency vehicle access, tractors, and similar equipment.
At 150-200mm (6-8 inches), the system handles under 30,000 kg for standard construction traffic and refuse vehicles.
At 200mm (8 inches), maximum capacity reaches under 50,000 kg for heavy construction traffic and up to 60,000 kg for HGV, crane, and piling rig applications.
Matching Depth to Application
The critical specification principle is to match depth to your heaviest regular load, not your average load. A parking lot that mostly serves passenger cars but receives weekly delivery truck visits needs specifications for delivery trucks. A fire lane that sits empty 364 days per year but must support fire apparatus on day 365 needs specifications for fire trucks.
BaseCore’s Selection Guide provides detailed recommendations by application type. Light applications like trails, bike lanes, and ATV paths use 2-3 inch depths. Non-industrial passenger vehicles and light industrial applications use 3-4 inch depths. Industrial applications with 18-wheelers, oil and gas, and mining operations use 4-6 inch depths. Heavy applications including fire trucks and H-20 loading require 6-8 inch depths.
For slope stabilization, depth recommendations increase with slope steepness. Gentle slopes of 6:1 to 5:1 use 2-3 inch depths. Moderate slopes of 4:1 use 3-4 inch depths. Steeper slopes of 3:1 use 4-inch depths. Aggressive slopes of 2:1 use 4-6 inch depths. The steepest applications of 1:1 or greater require 6-8 inch depths.
Technical Specifications and Certifications
BaseCore geocells meet rigorous industry standards that verify performance claims through standardized testing.
ASTM Compliance
BaseCore products conform to multiple ASTM standards that govern geosynthetic materials. ASTM D5199 governs sheet thickness measurement, with BaseCore HD measuring 65-75 mils before and after texturing. ASTM D6392 establishes seam peel strength requirements, which BaseCore exceeds with ratings of 1420 N to 2000 N depending on cell height. ASTM D1693 measures Environmental Stress Crack Resistance, where BaseCore HD achieves 7,000+ hours. ASTM D1505 verifies polymer density at 0.935 to 0.965 lb/ft³. ASTM D1603 confirms carbon black content of 1.5-2% for UV stability.
BaseCore meets ASTM D6818 and D6454 guidelines for geocell applications and carries ISO 9001 certified manufacturing status.
UV Resistance and Temperature Range
Per ASTM D4355 testing, BaseCore geocells retain 70% strength after 1,500 hours of UV exposure—important for applications where geocells remain exposed to sunlight before infill placement or where partial exposure continues in service.
The operating temperature range spans -50°C to 80°C (-58°F to 176°F), covering essentially any climate condition encountered in typical installations from extreme northern winters to desert summers.
Quality Assurance
Each manufacturing run undergoes testing for consistency in sheet thickness, seam weld strength, and physical properties. Every panel carries lot and batch numbers for quality tracking and traceability. This systematic quality control ensures that the geocells you receive match the specifications you ordered.
Panel Dimensions and Coverage
Geocells ship as collapsed panels that expand on-site into their three-dimensional honeycomb configuration. Understanding panel sizes helps you plan material quantities and installation logistics.
Stock Panel Sizes
BaseCore maintains stock panels in multiple sizes to fit most applications efficiently. Common stock sizes include configurations that expand to approximately 6.2 by 9 feet, 9 by 18 feet, 8 by 24 feet, and 9.4 by 24 feet depending on cell height and product line.
For the 2-inch BaseCore HD, stock panels expand to 6.2 by 9 feet. For 3-inch standard BaseCore, panels expand to 9.4 by 24 feet. For 3-inch BaseCore HD, options include 6.2 by 9 feet or 6.2 by 18 feet configurations. The 4-inch standard BaseCore expands to 9 by 18 feet, while 4-inch BaseCore HD expands to 8 by 24 feet.
Six-inch and 8-inch depths in both product lines are available upon request per project specifications.
Custom Panel Sizing
For projects where standard sizes create excessive waste from cutting to fit irregular boundaries, BaseCore can customize panel dimensions to match your specific geometry. This customization minimizes waste and reduces total material cost on projects where standard sizes would require significant trimming.
Coverage Calculations
Calculate your total square footage needs, then add 5-10% overage to account for cuts at boundaries, waste from irregular shapes, and occasional damaged panels. Running short during installation creates expensive delays waiting for additional material shipments.
Your BaseCore project manager will help you determine the most efficient panel configuration for your specific project geometry, balancing coverage efficiency against shipping logistics and installation practicality.
Perforations, Colors, and Options
Perforated vs. Non-Perforated
Standard BaseCore geocells feature perforations—small holes in the cell walls that allow water and roots to pass through laterally between cells. Perforated geocells serve most applications well. The perforations maintain drainage throughout the system, preventing water from being trapped within individual cells. For vegetated applications, roots spread through perforations to create more robust plant establishment.
Non-perforated geocells provide complete containment for applications using fine materials that might wash through perforations, or where maximum lateral confinement matters more than drainage. Non-perforated cells are available as special orders from BaseCore.
Color Options
Standard BaseCore geocells are black, which suits most applications where geocells become fully covered by infill material and invisible in the finished installation.
For applications where geocells remain partially visible or where color matching matters for aesthetic reasons, beige and green options are available. These alternative colors work well for landscaping applications, residential installations where appearance matters, or vegetated systems where geocell edges might be visible at the surface.
Infill Recommendations
The infill material you choose significantly affects performance. For most load-bearing applications, BaseCore recommends #57 crushed angular stone with 15-20% fines. The angular particles interlock within cells, creating stable surfaces. The fines content improves compaction and surface smoothness.
For erosion control and grass applications, topsoil allows vegetation to establish within the geocell structure. Some projects combine approaches—gravel in lower portions for load capacity with topsoil in upper layers for vegetation.
Real-World Applications
Understanding geocells conceptually is valuable. Seeing how actual projects apply them demonstrates practical value across diverse use cases.
Commercial Parking Lots
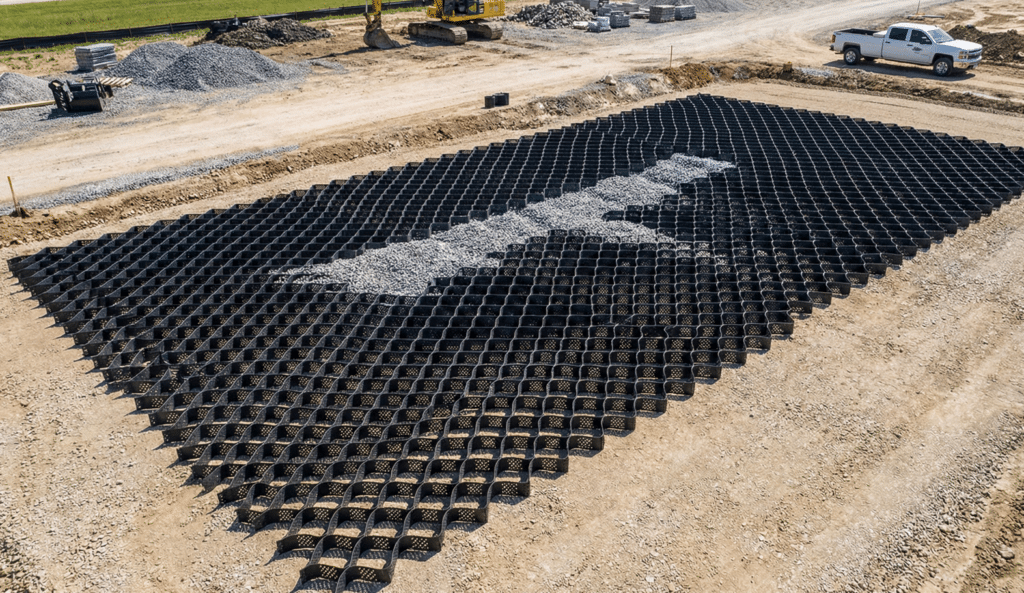
Parking lots represent the most common geocell application. A manufacturing facility needed 30,000 square feet of overflow parking within six weeks. Asphalt quotes exceeded budget by 40%, and the civil engineer’s site plan required a $28,000 detention basin for stormwater runoff from an impervious surface.
The BaseCore HD solution eliminated the detention basin entirely. Because geocell systems maintain over 90% permeability, stormwater infiltrates on-site rather than running off. Installation took nine days. The system handles daily semi-truck traffic. Five years later, the surface requires no maintenance.
Industrial and Heavy Equipment
A distribution center in Arizona spent $12,000 annually maintaining their traditional gravel yard. Every quarter, crews regraded and added fresh gravel. The BaseCore HD system with 8-inch cell depth handles loaded semi-truck traffic continuously. Five years post-installation, they haven’t regraded once.
Military and Government Applications
BaseCore HD’s commercial/military grade designation reflects actual military use. The double-welded seams, thicker material, and higher cell density handle the extreme loads and demanding conditions military operations require—the same engineering benefits that serve commercial and industrial applications.
Erosion Control
Beyond vehicle support, geocells solve erosion problems on slopes where other approaches fail. Highway embankments, residential hillsides, drainage channels, and detention basin slopes benefit from geocell erosion control. The cells hold soil in place during the critical vegetation establishment period. Once root systems develop, the combination of cellular confinement and natural root structure creates permanent stabilization.
Emergency Vehicle Access
Fire codes often require emergency vehicle access through areas owners prefer to maintain as green space. Geocells filled with soil and seeded with grass remain green during normal conditions while supporting fire trucks when needed.
Installation Overview
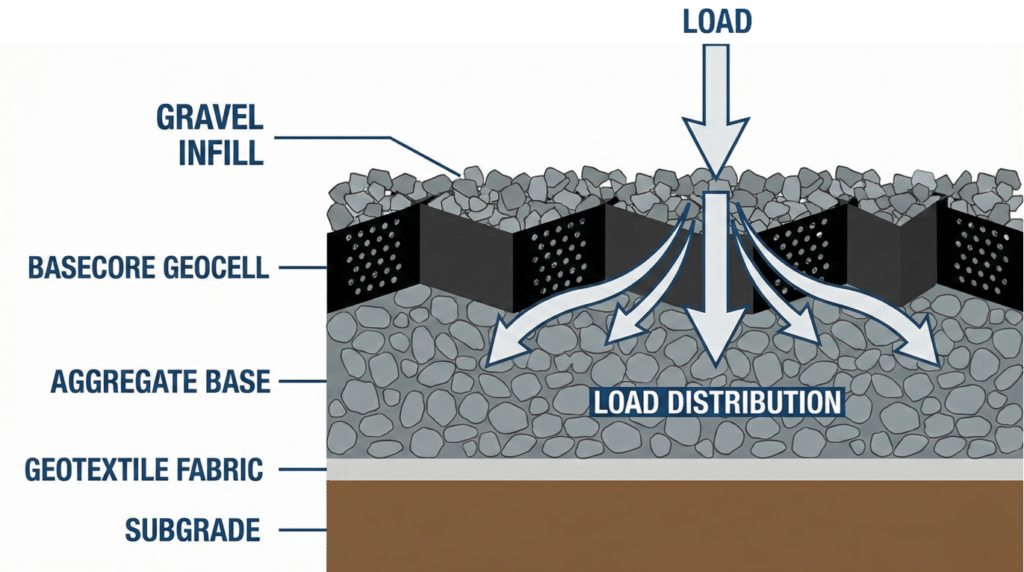
Geocell installation is more structured than spreading loose gravel but far simpler than paving.
Site Preparation
Every successful installation starts with proper site preparation. The prepared surface must be graded for drainage—minimum 2% slope—and smooth enough that panels lie flat without bridging over depressions.
For load-bearing applications, a compacted aggregate base course provides the stable platform. Base course thickness varies by application: 4-6 inches for light-duty, 6-8 inches for medium-duty, and 8-12 inches for heavy-duty installations.
A geotextile fabric layer between subgrade and aggregate base prevents soil contamination. BaseCore recommends 6-12 oz non-woven geotextile depending on application requirements.
Panel Installation
Panels expand from their collapsed shipping configuration into three-dimensional honeycomb shapes on-site. Once expanded, panels connect using the BaseClip connection system. Proper connection distributes loads across multiple panels rather than concentrating stress at edges.
An experienced four-person crew can install approximately 10,000 square feet per day on a prepared surface.
Infill and Compaction
After panel expansion and connection, cells are filled with infill material. All cells must be filled 1-2 inches above cell walls before compacting. Final compaction uses a three-ton-plus vibratory roller with water application during compaction.
The surface is immediately usable after compaction—no curing time required.
Labor Costs
Installation labor typically runs $0.50-$1.00 per square foot depending on site complexity and regional rates. BaseCore can quote installation on some projects, work alongside your contractor, or refer experienced installers in your region.
Working with BaseCore
Getting Started
Request a quote at basecore.co/quick-basecore-quote with your project information. Include approximate square footage, intended application, vehicle types the surface will support, and your timeline.
A BaseCore project manager will discuss specifications, quantities, and pricing. Most standard products ship from stock. Larger or special orders may require up to six weeks. There’s no minimum order size.
Warranty
BaseCore geocells include a 10-year warranty covering product and seam strength. The HDPE material itself is engineered to provide 75+ years of ground stabilization based on material science and degradation characteristics.
Support Resources
Installation guides, technical documentation, and spec sheets are available on the website and upon request. Phone support is available for project questions throughout your installation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do geocells actually last?
BaseCore geocells are engineered from 100% virgin HDPE to provide 75+ years of ground stabilization based on material science. The 10-year warranty covers product and seam strength, while the material itself far outlasts typical project lifecycles.
What’s the difference between BaseCore and BaseCore HD?
BaseCore HD is the commercial/military grade with 2.4mm thick material (vs 1.7mm), double-welded seams, 35% higher cell density, and tensile strength exceeding 2,000 lbs/sq ft. Standard BaseCore suits residential applications; HD suits commercial, industrial, and demanding applications.
Can geocells handle snow plowing?
Yes. The cellular structure sits below finished surface level once properly filled and compacted. Snow plows pass over without catching. Freeze-thaw cycles don’t damage properly installed systems with adequate drainage.
What makes BaseCore different from other geocells?
BaseCore uses 100% virgin HDPE with thicker material and double-welded seams (HD product). Many alternatives use thinner materials or recycled content that compromises long-term performance. BaseCore HD achieves 7,000 hours Environmental Stress Crack Resistance versus 5,000-6,000 typical of alternatives.
Can I install geocells myself?
DIY installation is feasible for smaller projects if you have construction experience, proper compaction equipment access, and helpers available. BaseCore provides detailed installation guides. Professional installation is recommended for larger or complex projects.
Taking the Next Step
The logistics facility that opened this guide represents thousands of similar success stories. Organizations tired of the maintenance treadmill of traditional gravel, the cost premium of asphalt, or failed promises of inadequate solutions discover that properly engineered geocells deliver lasting performance—75+ years of ground stabilization from a single installation.
If your project fits these applications, request a quote. A project manager will help you evaluate specifications, recommend the right BaseCore or BaseCore HD system, and provide accurate pricing. No pressure, no obligation—just expert guidance from people who’ve helped thousands of property owners solve these challenges permanently.
